Understanding Hypertension and It's Impact on Lung Health and Effective Methods to Build Strong Lung
Lung health is a vital component of overall well-being, and maintaining strong lungs can have a profound impact on longevity. This article explores the connection between hypertension and lung health, highlighting the importance of strong lungs for a longer life. Additionally, we delve into effective methods and exercises to build stronger lungs, empowering individuals to prioritize and enhance their respiratory fitness.
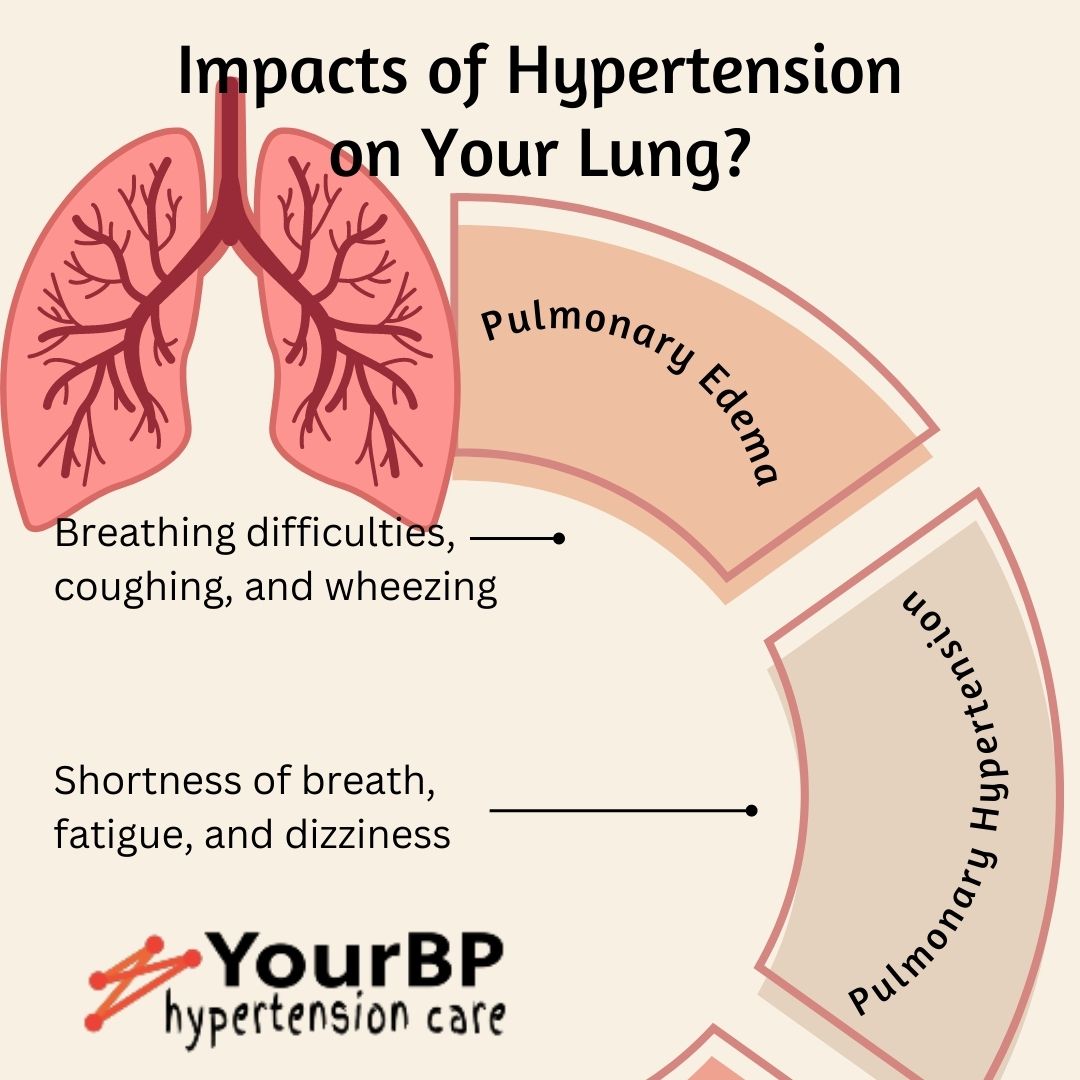
Understanding Hypertension and Its Impact on Lung Health
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a chronic medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the force of blood against the walls of the arteries is consistently too high. While hypertension primarily affects the cardiovascular system, it can also have a significant impact on lung health.
When hypertension is left uncontrolled, it can contribute to the development of various lung-related complications. One such complication is pulmonary hypertension, a condition characterized by increased pressure in the pulmonary arteries that supply blood to the lungs. In pulmonary hypertension, the arteries narrow and thicken, which can lead to restricted blood flow and strain on the right side of the heart. Over time, this can impair the proper functioning of the lungs and result in symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and dizziness.
In addition to pulmonary hypertension, uncontrolled hypertension can also contribute to the development of pulmonary edema. Pulmonary edema occurs when excess fluid accumulates in the lungs, leading to breathing difficulties, coughing, and wheezing. Elevated blood pressure can weaken the blood vessels in the lungs, causing them to leak fluid into the surrounding lung tissue. This fluid accumulation interferes with the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide, impairing lung function and reducing the body's overall oxygen supply.
By effectively managing hypertension, individuals can minimize the risk of developing pulmonary complications, maintain proper lung function, and support overall respiratory well-being. Regular monitoring, adherence to prescribed treatment plans, and a proactive approach to lifestyle choices are key to mitigating the impact of hypertension on lung health.
The Significance of Strong Lungs for Longevity
Lung capacity and longevity: Research has demonstrated that lung capacity, which refers to the maximum amount of air the lungs can hold, is closely linked to longevity. Individuals with greater lung capacity tend to have a lower risk of mortality and a higher quality of life.
Oxygen supply and vitality: Strong lungs efficiently deliver oxygen to the body's tissues and organs, ensuring optimal functioning. This oxygen-rich environment supports energy production, immune system strength, and overall vitality.
Methods to Build Stronger Lungs
Regular aerobic exercise:
Engaging in aerobic exercises is one of the most effective ways to improve lung strength and capacity. Activities such as brisk walking, running, cycling, swimming, and dancing promote deep breathing and increase lung ventilation, enhancing lung function over time.Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous aerobic exercise per week.
Breathing exercises:
Specific breathing techniques can strengthen the respiratory muscles and improve lung function.Diaphragmatic breathing, also known as belly breathing, involves deep inhalations that fully expand the diaphragm and enhance lung capacity.
Other practices such as pursed lip breathing and alternate nostril breathing can also improve respiratory efficiency and lung health.
Strength training:
While aerobic exercise primarily targets cardiovascular fitness, incorporating strength training exercises into your routine can indirectly benefit lung health.Strengthening the muscles in your chest, back, and core improves posture and provides support to the lungs, facilitating optimal breathing mechanics.
Yoga and tai chi:
Yoga and tai chi emphasize controlled breathing, relaxation, and mindful movement, promoting lung health. These practices improve lung capacity, enhance respiratory muscle strength, and encourage deep and controlled breathing patterns.Best Exercises for Lung Health
- Cardiovascular exercises:
- Jogging or running
- Cycling
- Swimming
- High-intensity interval training (HIIT)
- Aerobic dance or Zumba
- Interval training:
- Incorporating intervals of intense exercise followed by periods of active recovery can challenge and strengthen the respiratory system.
- For example, alternating between sprinting and walking or cycling at different intensities.
- Stair climbing:
- Climbing stairs is a vigorous activity that engages the lungs and helps build lung capacity and strength.
- Take the stairs whenever possible or use a stair-climbing machine at the gym.
- Lunges and squats:
- These lower body exercises engage multiple muscle groups, including those involved in respiration.
- Lunges and squats require controlled breathing and promote improved lung function.
Conclusion
Strong lungs play a significant role in overall health and longevity. The connection between hypertension and lung health underscores the importance of maintaining optimal blood pressure levels for respiratory well-being. By adopting effective methods such as regular aerobic exercise, breathing exercises, strength training, and engaging in lung-enhancing activities, individuals can build stronger lungs, improve lung capacity, and enhance their overall health and longevity. Prioritizing lung health today sets the foundation for a longer, more vibrant life tomorrow.Reference: pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, mayoclinic.org
Manage your hypertension with YourBP's first of it's kind -- self-care app.
Get it on your Phone
In this Article
- Understanding Hypertension and Its Impact on Lung Health
- The Significance of Strong Lungs for Longevity
- Methods to Build Stronger Lungs
- Best Exercises for Lung Health
- Conclusion
Also Read
- Are Migraine Patients at Increased Risk of Developing Hypertension?
- Hypertension: Long-Term Consequences and Symptoms
- Natural Ways to Lower High Blood Pressure: Exercise, Yoga, and a Healthy Diet
- Safer Birth Control Methods for People with High Blood Pressure & Cholesterol
- Unveiling the Hidden Clues: Kidney Disease, Hypertension, and Urine Proteins Link
