Harnessing the Power of the DASH Diet: An Effective Strategy for Controlling Hypertension and Diabetes
High blood pressure and diabetes are two prevalent health conditions that affect millions of individuals worldwide. Both conditions require careful management and lifestyle modifications to prevent complications and maintain overall well-being. One approach that has gained considerable recognition for its effectiveness in managing both high blood pressure and diabetes is the DASH diet. This article will delve into the details of the DASH diet, exploring its principles, benefits, and how it can help individuals improve their health.
Understanding the DASH Diet
DASH stands for Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension, which originally aimed to help individuals lower their blood pressure. However, studies have shown that the DASH diet can also be beneficial for people with diabetes. The diet emphasizes consuming nutrient-rich foods while reducing the intake of sodium, saturated fats, and cholesterol.
Principles of the DASH Diet
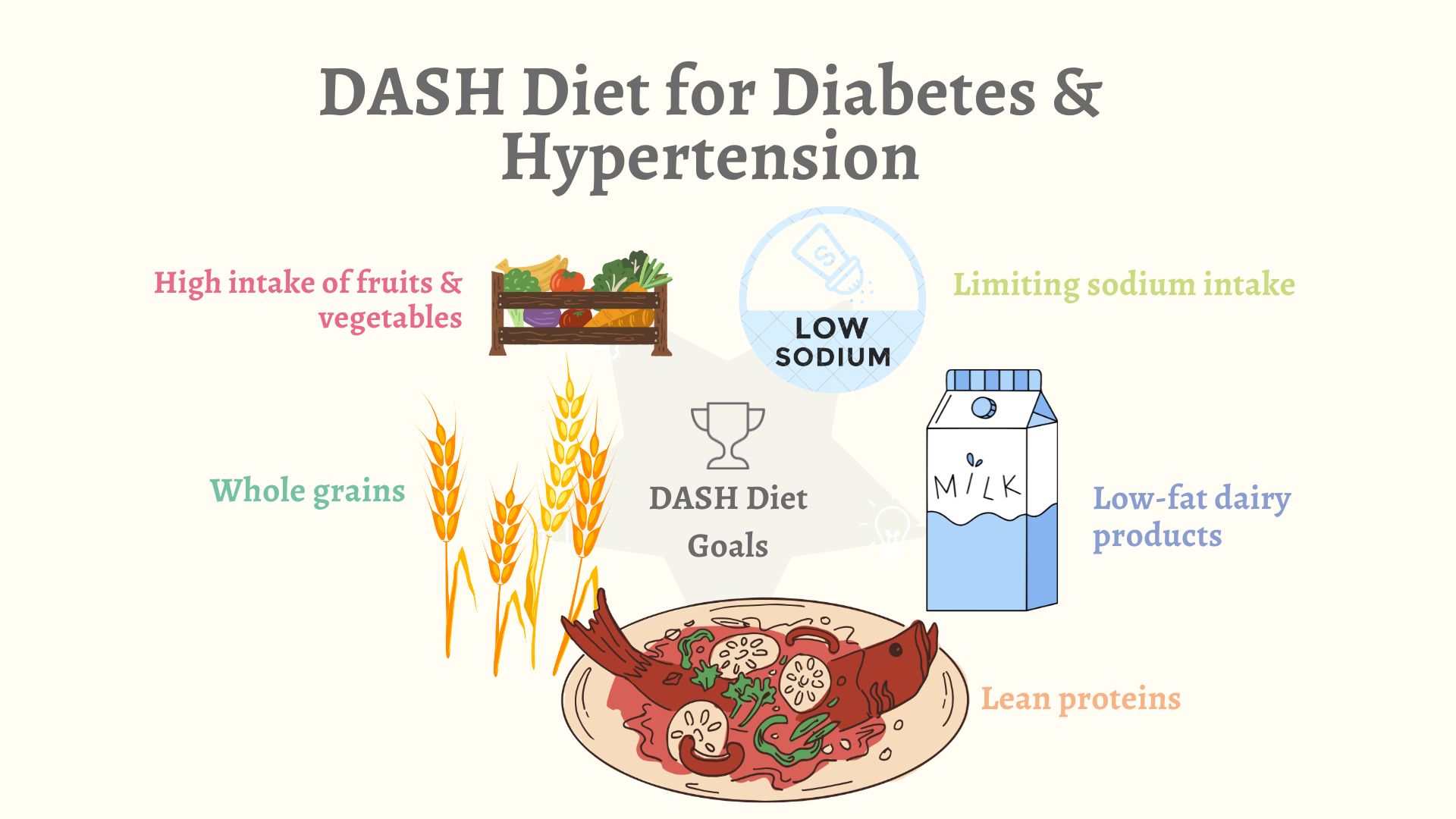
High intake of fruits and vegetables: The DASH diet encourages individuals to include a variety of fruits and vegetables in their daily meals. These foods are rich in essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber, which contribute to overall health and well-being.
Whole grains: Opting for whole grains such as brown rice, whole wheat bread, and oatmeal is preferred over refined grains. Whole grains are high in fiber and provide a slower release of energy, helping to control blood sugar levels and maintain a healthy weight.
Lean proteins: The DASH diet suggests including lean proteins in meals, such as skinless poultry, fish, beans, nuts and legumes. These protein sources are low in saturated fat and cholesterol, making them heart-healthy choices.
Low-fat dairy products: Consuming low-fat or fat-free dairy products, like milk, yogurt, and cheese, is recommended in moderate amounts. These provide calcium, vitamin D, and other essential nutrients without excessive fat content.
Limiting sodium intake: The DASH diet places strong emphasis on reducing sodium intake. High levels of sodium can lead to increased blood pressure, so it's important to minimize processed and packaged foods, which are often high in sodium. Instead, individuals are encouraged to flavor meals with herbs and spices.
Benefits of the DASH Diet
Blood pressure management: The DASH diet's primary objective is to reduce high blood pressure, which is a significant risk factor for heart disease and stroke. By following the DASH diet, individuals can experience lower blood pressure levels and potentially reduce their need for medication.
Diabetes control: The DASH diet's emphasis on whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, along with its limited sodium intake, can help individuals with diabetes manage their blood sugar levels effectively. The fiber-rich foods promote slower digestion and prevent blood sugar spikes, supporting overall glycemic control.
Weight management: The DASH diet promotes the consumption of nutrient-dense foods while reducing calorie-dense options. The inclusion of lean proteins and whole grains helps individuals feel satiated for longer periods, which can contribute to weight management and reduce the risk of obesity-related complications.
Reduced risk of cardiovascular disease: By following the DASH diet, individuals can improve their heart health by reducing their intake of saturated fats and cholesterol. This, combined with the diet's focus on nutrient-rich foods, can lower the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases.
Implementing the DASH Diet
To adopt the DASH diet effectively, consider the following steps:
Consult your healthcare provider: Before making any significant changes to your diet, it's essential to consult with your healthcare provider, particularly if you have existing health conditions or take specific medications.
Gradual transition: Rather than drastically altering your eating habits, aim for a gradual transition towards the DASH diet. Start by incorporating more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains into your meals while reducing processed and high-sodium foods.
Meal planning: Plan your meals in advance to ensure that you are meeting the recommendations of the DASH diet. Create a grocery list that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy products.
Be mindful of sodium: Read food labels carefully to identify sodium content and opt for low-sodium or sodium-free alternatives. Avoid adding excessive salt to your meals and experiment with herbs and spices to enhance flavor instead.
Track progress: Keep a record of your blood pressure and blood sugar levels to monitor the impact of the DASH diet on your health. This information can also help your healthcare provider make any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
Conclusion
The DASH diet offers a valuable approach to managing high blood pressure and diabetes simultaneously. By emphasizing nutrient-rich foods, limiting sodium intake, and focusing on whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, individuals can experience improved blood pressure control, better diabetes management, and a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease. As with any dietary changes, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional to personalize the DASH diet according to individual needs and health conditions. By embracing the DASH diet, individuals can take proactive steps towards achieving better health and well-being.
Reference:
abbott,
webmd,
healthline
Manage your hypertension, diabetes and general wellness tracking with YourBP's first of it's kind health tracking app.
Get it on your Phone
In this Article
- Understanding the DASH Diet
- Principles of the DASH Diet
- Benefits of the DASH Diet
- Implementing the DASH Diet
- Conclusion
